
”Here, little fishies! Come get your poison!”
Fugu, as pufferfish is called in Japan, is famous for two things it can do: make your taste buds rejoice and flat-out kill you. That’s because fugu livers, ovaries, eyes, and even skin contain tetrodotoxin, a powerful neurotoxin that causes paralysis, leaving those afflicted by the poison, for which there is no known antidote, to suffocate.
However, fugu don’t produce tetrodotoxin themselves. Instead, they acquire it through eating other sea creatures that contain bacteria with tetrodotoxin in smaller amounts, developing a resistance to the harmful effects in the process. So though fugu in the wild naturally gravitate towards a diet that leads to tetrodotoxin permeating their skin and organs, if their diet from birth was limited to foods without those bacteria, you’d have non-poisonous fugu.
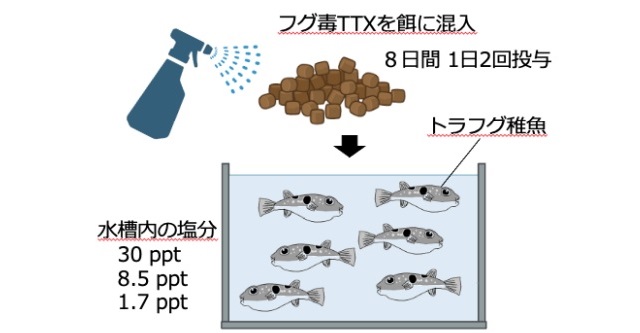
But what if you took some non-poisonous fugu, who’d been hatched and then raised in a research facility and were thus tetrodotoxin-free, and started feeding them tetrodotoxin? That’s the question being asked by scientists at Nagasaki University, who’ve started mixing a dose of tetrodotoxin in with the feed for a group of non-poisonous fugu.
▼ A diagram of the experiment (hopefully the spray bottle of neurotoxin is very clearly labeled so that no one mistakes it for Febreze)
To answer the most immediate question that springs to mind, the fugu haven’t died, as apparently the dosage is small enough to not be life-threatening. However, the researchers have observed changes in the composition of the fugu’s intestinal flora, i.e. their gut bacteria. These changes could also possibly affect the functions of the fugu’s gut microbiome relating to metabolizing lipids and sugars. Whether these changes have a positive or negative effect on the fugu’s wellbeing is a question the researchers say will require further study to answer.
Another question that might be springing to mind is “Why?” Why, after going to the trouble to raise non-poisonous pufferfish, would you think “OK, let’s poison these guys up!”? The goal is to better understand fugu physiology in order to apply that knowledge to aquaculture. Though non-toxic fugu were first bred more than 20 years ago (also by scientists at Nagasaki University), farm-raised fugu is yet to really catch on among foodies, leaving demand for the fish to be supplied almost entirely on wild catches. Being able to more effectively raise fugu, with a flavor replicating that of wild-caught fish, could lessen the environmental impact of the pufferfish-eating practice.
The researchers say they should have further results ready for public announcement next summer.
Source: TBS News Dig via Jin, Nagasaki University
Images: Nagasaki University
● Want to hear about SoraNews24’s latest articles as soon as they’re published? Follow us on Facebook and Twitter!

 Treat Yourself to this Japanese Delicacy if You Dare – Ovaries From a Poisonous Fish!
Treat Yourself to this Japanese Delicacy if You Dare – Ovaries From a Poisonous Fish! Aichi supermarket caught selling poisonous puffer fish livers, “been selling it for decades”
Aichi supermarket caught selling poisonous puffer fish livers, “been selling it for decades” Nagoya man hospitalized after eating fish with name including “fugu,” a.k.a. “poisonous blowfish”
Nagoya man hospitalized after eating fish with name including “fugu,” a.k.a. “poisonous blowfish” 10-year-old Japanese girl is youngest person ever certified to prepare deadly poisonous blowfish
10-year-old Japanese girl is youngest person ever certified to prepare deadly poisonous blowfish We eat fugu pufferfish semen at a Japanese restaurant in Tokyo
We eat fugu pufferfish semen at a Japanese restaurant in Tokyo Studio Ghibli releases Catbus pullback keychain that runs like the anime character
Studio Ghibli releases Catbus pullback keychain that runs like the anime character Giant pipe mysteriously rises up through street in downtown Osaka
Giant pipe mysteriously rises up through street in downtown Osaka As rumors swirl of 7-Eleven shorting customers on rice ball fillings, we check on their sujiko
As rumors swirl of 7-Eleven shorting customers on rice ball fillings, we check on their sujiko Nine great places to see spring flowers in Japan, as chosen by travelers (with almost no sakura)
Nine great places to see spring flowers in Japan, as chosen by travelers (with almost no sakura) Private open-air bath is the crowning gem at this Japanese-style hotel in Tokyo
Private open-air bath is the crowning gem at this Japanese-style hotel in Tokyo Man in Japan falls into hole with a bear in it
Man in Japan falls into hole with a bear in it Is Daiso’s microwave Japanese rolled omelet maker worth your time and money? [Taste test]
Is Daiso’s microwave Japanese rolled omelet maker worth your time and money? [Taste test] Starbucks Japan unveils new sakura cherry blossom collection for hanami season 2026
Starbucks Japan unveils new sakura cherry blossom collection for hanami season 2026 Deceptive strawberry milk package angers 7-Eleven customers following banana scandal
Deceptive strawberry milk package angers 7-Eleven customers following banana scandal Burger King Japan’s Great King Yeti is the latest evolution of One Pounders
Burger King Japan’s Great King Yeti is the latest evolution of One Pounders Japanese government planning higher ticket prices for foreign tourists at Tokyo National Museum
Japanese government planning higher ticket prices for foreign tourists at Tokyo National Museum Starbucks Japan releases a new Cream Puff Frappuccino for a limited time
Starbucks Japan releases a new Cream Puff Frappuccino for a limited time Silicone testicle covers banned from Japanese sauna following cups being left behind and on shelves
Silicone testicle covers banned from Japanese sauna following cups being left behind and on shelves Studio Ghibli now sells Ursula’s backpack from Kiki’s Delivery Service at its anime shop in Japan
Studio Ghibli now sells Ursula’s backpack from Kiki’s Delivery Service at its anime shop in Japan Is Japan’s Crab-shaped Cup Ramen Timer worth the hype?
Is Japan’s Crab-shaped Cup Ramen Timer worth the hype? Starbucks Japan opens new cafe and art gallery in top Tokyo tourist neighbourhood
Starbucks Japan opens new cafe and art gallery in top Tokyo tourist neighbourhood Pizza Hut Japan teams up with creator of one of the country’s best kinds of ramen for ramen pizza
Pizza Hut Japan teams up with creator of one of the country’s best kinds of ramen for ramen pizza Mister Donut unveils new sakura doughnuts for cherry blossom season 2026
Mister Donut unveils new sakura doughnuts for cherry blossom season 2026 Japan’s newest Shinkansen has no seats…or passengers [Video]
Japan’s newest Shinkansen has no seats…or passengers [Video] Starbucks Japan releases new sakura goods and drinkware for cherry blossom season 2026
Starbucks Japan releases new sakura goods and drinkware for cherry blossom season 2026 Foreigners accounting for over 80 percent of off-course skiers needing rescue in Japan’s Hokkaido
Foreigners accounting for over 80 percent of off-course skiers needing rescue in Japan’s Hokkaido Super-salty pizza sends six kids to the hospital in Japan, linguistics blamed
Super-salty pizza sends six kids to the hospital in Japan, linguistics blamed Starbucks Japan unveils new sakura Frappuccino for cherry blossom season 2026
Starbucks Japan unveils new sakura Frappuccino for cherry blossom season 2026 Foreign tourists in Japan will get free Shinkansen tickets to promote regional tourism
Foreign tourists in Japan will get free Shinkansen tickets to promote regional tourism The 10 most annoying things foreign tourists do on Japanese trains, according to locals
The 10 most annoying things foreign tourists do on Japanese trains, according to locals Naruto and Converse team up for new line of shinobi sneakers[Photos]
Naruto and Converse team up for new line of shinobi sneakers[Photos] Take a trip to Japan’s Dododo Land, the most irritating place on Earth
Take a trip to Japan’s Dododo Land, the most irritating place on Earth Survey asks foreign tourists what bothered them in Japan, more than half gave same answer
Survey asks foreign tourists what bothered them in Japan, more than half gave same answer Japan’s human washing machines will go on sale to general public, demos to be held in Tokyo
Japan’s human washing machines will go on sale to general public, demos to be held in Tokyo Starbucks Japan releases new drinkware and goods for Valentine’s Day
Starbucks Japan releases new drinkware and goods for Valentine’s Day We deeply regret going into this tunnel on our walk in the mountains of Japan
We deeply regret going into this tunnel on our walk in the mountains of Japan Studio Ghibli releases Kodama forest spirits from Princess Mononoke to light up your home
Studio Ghibli releases Kodama forest spirits from Princess Mononoke to light up your home Major Japanese hotel chain says reservations via overseas booking sites may not be valid
Major Japanese hotel chain says reservations via overseas booking sites may not be valid Put sesame oil in your coffee? Japanese maker says it’s the best way to start your day【Taste test】
Put sesame oil in your coffee? Japanese maker says it’s the best way to start your day【Taste test】 No more using real katana for tourism activities, Japan’s National Police Agency says
No more using real katana for tourism activities, Japan’s National Police Agency says Picture of a pufferfish vomiting water is the Japanese Internet’s newest darling
Picture of a pufferfish vomiting water is the Japanese Internet’s newest darling