
Ningyo was said to have been pulled out of the sea by a fisherman in Tosa domain nearly 300 years ago.
Much like how the dragons of Japanese lore differ from their European counterparts, Japanese mermaids look very different from what you you’ll see in a Hans Christian Andersen storybook or Disney movie. Japan’s ningyo (which translates literally as “people fish”) are often depicted not with the upper body of a supermodel, but a more compact, almost simian form.
If you’re having trouble forming a mental image, perhaps this video will help and/or give you nightmares.
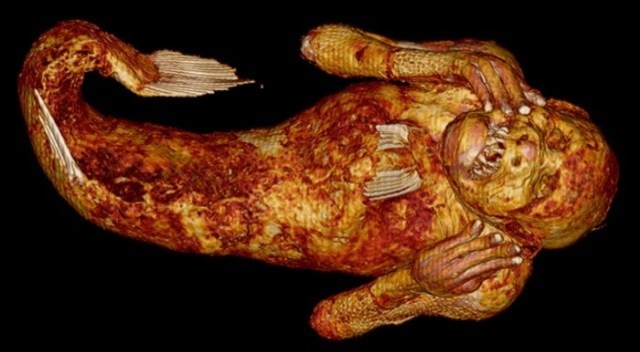
Shown in the video is one of the treasures stored at Enjuin Temple in the town of Asakuchi, Okayama Prefecture. According to a handwritten note inside the paulownia box in which it’s been stored, it’s the mummified body of a ningyo that was caught in a fisherman’s net in the waters off Tosa (present-day Kochi Prefecture) during the Genbun era of Japanese history, which lasted from 1736 to 1741.
▼ Enjuin’s mermaid mummy
However, no one is exactly sure how the temple came to be in possession of the mermaid mummy, which doesn’t exactly help the tale’s plausibility. In February of last year a five-person team of researchers from Kurashiki University of Science and the Arts, also in Okayama, began an investigation to determine the true identity of the artifact through X-rays, CT scans, DNA analysis, and radiocarbon dating.
ツイートが遅れましたが2022年2/2〜倉敷芸術科学大学が調査していた円珠院 #人魚のミイラ の研究中間報告が発表されています。併せてお知らせのように7/16〜9/25倉敷市立自然史博物館で展示します。
— パオちゃん(倉敷市立自然史博物館) (@kura_n_h_museum) April 8, 2022
円珠院所蔵「人魚のミイラ」研究中間報告(2022.04.04) | 倉敷芸術科学大学https://t.co/yTIcvyWxkS pic.twitter.com/nA9DFOno6s
This week the team announced its results, and unfortunately for cryptid fans, no, it turns out it’s not actually a mermaid. The KUSA team knew something was up when the only genuine skeletal structure component they could confirm was a jawbone, as the 30-centimeter (11.8-inch) “ningyo” lacked a skull, spine, or ribs.
Instead, the investigation found that the artifact was crafted from a plaster or gypsum-like substance, from which features including its arms, hands, and eye sockets were formed. The upper body, which also had portions made of cloth, was wrapped in a thin sheet of paper, which was then wrapped in fugu (blowfish) skin, and the head was stuffed with cotton with some sort of indeterminate animal hair attached to the top of the head to give it a mammalian appearance. The scales and fins on the lower body, meanwhile, appear to be from a species of croaker fish. Even the part about the artifact being found in a fisherman’s net circa 1740 appears to be a hoax, as the researchers, after examining some scales that fell off of the lower-body portion, calculated that the ningyo carcass was most likely from the latter half of the 1800s.
However, the temple isn’t upset about having been duped. Speaking after the researchers announced their results, Enjuin abbot Hiroyoshi Kuida said “I think, because of the tale, many people have come to see the ningyo [when it is on display], and prayed while they are here, and I think they’ll continue to do so,” adding, “Knowing that it was made from living things, we will continue to take good care of it and keep it safe.”
▼ Hiroyoshi Kuida can be seen in this clip
It’s worth pointing out that ningyo aren’t prescribed any special religious significance in Japanese Buddhism, so the revelation that Enjuin’s isn’t real is unlikely to trigger any crises of faith or drop in visitors to the temple.
Sources: Asahi Shimbun via Livedoor News via Hachima Kiko, Kurashiki University of Science and the Arts, @Press
Top image: Pakutaso
Insert image: @Press
● Want to hear about SoraNews24’s latest articles as soon as they’re published? Follow us on Facebook and Twitter!

 Japanese voodoo dolls with foreign politician photo keep getting nailed to town’s shrine trees
Japanese voodoo dolls with foreign politician photo keep getting nailed to town’s shrine trees Batman as a samurai ningyo figure is trans-Pacific time-tripping awesomeness
Batman as a samurai ningyo figure is trans-Pacific time-tripping awesomeness Starbucks Reserve Roastery sells lucky Japanese figurines to ring in 2023
Starbucks Reserve Roastery sells lucky Japanese figurines to ring in 2023 Hatsune Miku becomes classic hina doll to show girls they don’t have to get married to be happy
Hatsune Miku becomes classic hina doll to show girls they don’t have to get married to be happy Charges dropped against elderly Japanese man for nailing Putin voodoo doll to sacred shrine tree
Charges dropped against elderly Japanese man for nailing Putin voodoo doll to sacred shrine tree Seaside scenery, history, and so many desserts on Yokohama’s Akai Kutsu【Japan Loop Buses】
Seaside scenery, history, and so many desserts on Yokohama’s Akai Kutsu【Japan Loop Buses】 Foreigner’s request for help in Tokyo makes us sad for the state of society
Foreigner’s request for help in Tokyo makes us sad for the state of society Japanese city loses residents’ personal data, which was on paper being transported on a windy day
Japanese city loses residents’ personal data, which was on paper being transported on a windy day Red light district sushi restaurant in Tokyo shows us just how wrong we were about it
Red light district sushi restaurant in Tokyo shows us just how wrong we were about it Ghibli Park now selling “Grilled Frogs” from food cart in Valley of Witches
Ghibli Park now selling “Grilled Frogs” from food cart in Valley of Witches Princesses, fruits, and blacksmiths: Study reveals the 30 most unusual family names in Japan
Princesses, fruits, and blacksmiths: Study reveals the 30 most unusual family names in Japan Should you add tartar sauce to Japanese curry rice? CoCo Ichi makes diners an unusual offer
Should you add tartar sauce to Japanese curry rice? CoCo Ichi makes diners an unusual offer Japan’s massive matcha parfait weighs 6 kilos, contains hidden surprises for anyone who eats it
Japan’s massive matcha parfait weighs 6 kilos, contains hidden surprises for anyone who eats it We try out “Chan Ramen”, an underground type of ramen popular in the ramen community
We try out “Chan Ramen”, an underground type of ramen popular in the ramen community Starbucks Japan releases new mugs and gifts for Mother’s Day
Starbucks Japan releases new mugs and gifts for Mother’s Day McDonald’s new Happy Meals offer up cute and practical Sanrio lifestyle goods
McDonald’s new Happy Meals offer up cute and practical Sanrio lifestyle goods Japanese ramen restaurants under pressure from new yen banknotes
Japanese ramen restaurants under pressure from new yen banknotes French Fries Bread in Tokyo’s Shibuya becomes a hit on social media
French Fries Bread in Tokyo’s Shibuya becomes a hit on social media Studio Ghibli releases new action figures featuring Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind characters
Studio Ghibli releases new action figures featuring Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind characters New private rooms on Tokaido Shinkansen change the way we travel from Tokyo to Kyoto
New private rooms on Tokaido Shinkansen change the way we travel from Tokyo to Kyoto Tokyo Tsukiji fish market site to be redeveloped with 50,000-seat stadium, hotel, shopping center
Tokyo Tsukiji fish market site to be redeveloped with 50,000-seat stadium, hotel, shopping center Beautiful Ghibli sealing wax kits let you create accessories and elegant letter decorations【Pics】
Beautiful Ghibli sealing wax kits let you create accessories and elegant letter decorations【Pics】 Studio Ghibli releases Kiki’s Delivery Service chocolate cake pouches in Japan
Studio Ghibli releases Kiki’s Delivery Service chocolate cake pouches in Japan New definition of “Japanese whiskey” goes into effect to prevent fakes from fooling overseas buyers
New definition of “Japanese whiskey” goes into effect to prevent fakes from fooling overseas buyers Our Japanese reporter visits Costco in the U.S., finds super American and very Japanese things
Our Japanese reporter visits Costco in the U.S., finds super American and very Japanese things All-you-can-drink Starbucks and amazing views part of Tokyo’s new 170 meter-high sky lounge
All-you-can-drink Starbucks and amazing views part of Tokyo’s new 170 meter-high sky lounge More foreign tourists than ever before in history visited Japan last month
More foreign tourists than ever before in history visited Japan last month New Pokémon cakes let you eat your way through Pikachu and all the Eevee evolutions
New Pokémon cakes let you eat your way through Pikachu and all the Eevee evolutions Disney princesses get official manga makeovers for Manga Princess Cafe opening in Tokyo
Disney princesses get official manga makeovers for Manga Princess Cafe opening in Tokyo Sales of Japan’s most convenient train ticket/shopping payment cards suspended indefinitely
Sales of Japan’s most convenient train ticket/shopping payment cards suspended indefinitely Sold-out Studio Ghibli desktop humidifiers are back so Totoro can help you through the dry season
Sold-out Studio Ghibli desktop humidifiers are back so Totoro can help you through the dry season Japanese government to make first change to romanization spelling rules since the 1950s
Japanese government to make first change to romanization spelling rules since the 1950s Ghibli founders Toshio Suzuki and Hayao Miyazaki contribute to Japanese whisky Totoro label design
Ghibli founders Toshio Suzuki and Hayao Miyazaki contribute to Japanese whisky Totoro label design Doraemon found buried at sea as scene from 1993 anime becomes real life【Photos】
Doraemon found buried at sea as scene from 1993 anime becomes real life【Photos】 Tokyo’s most famous Starbucks is closed
Tokyo’s most famous Starbucks is closed One Piece characters’ nationalities revealed, but fans have mixed opinions
One Piece characters’ nationalities revealed, but fans have mixed opinions We asked a Uniqlo employee what four things we should buy and their suggestions didn’t disappoint
We asked a Uniqlo employee what four things we should buy and their suggestions didn’t disappoint Lingerie for girls with smaller breasts: feast’s new collection “Glossy Ribbon Mermaid” is too cute
Lingerie for girls with smaller breasts: feast’s new collection “Glossy Ribbon Mermaid” is too cute Electronic grandchild “Ami-chan” developed by Takara Tomy
Electronic grandchild “Ami-chan” developed by Takara Tomy The long road of the Chusonji Lotus spans nearly a millennium of Japanese history
The long road of the Chusonji Lotus spans nearly a millennium of Japanese history Japan’s high-speed Shinkansen train makes emergency stop as snake is found onboard
Japan’s high-speed Shinkansen train makes emergency stop as snake is found onboard Japanese son handmakes Buddhist altar for deceased mother out of deeply touching materials
Japanese son handmakes Buddhist altar for deceased mother out of deeply touching materials Girl so scarred by souvenir from Tokyo Tower Aquarium that she doesn’t want to go to school
Girl so scarred by souvenir from Tokyo Tower Aquarium that she doesn’t want to go to school Flooded disaster-struck region in Japan urges people to use hashtag to tell everyone they’re okay
Flooded disaster-struck region in Japan urges people to use hashtag to tell everyone they’re okay Starbucks mermaid Frappuccino surfaces, makes waves online
Starbucks mermaid Frappuccino surfaces, makes waves online Shocking cat graffiti at centuries-old Japanese temple is shockingly uncute【Video】
Shocking cat graffiti at centuries-old Japanese temple is shockingly uncute【Video】 Just when you thought anime marketing couldn’t be any more bust-focused: character breast weights
Just when you thought anime marketing couldn’t be any more bust-focused: character breast weights The Star Wars folding screens just unveiled at Kyoto’s Kiyomizu Temple are amazing
The Star Wars folding screens just unveiled at Kyoto’s Kiyomizu Temple are amazing Japan’s Kanji of the Year revealed, reflects both the good and the bad of 2022
Japan’s Kanji of the Year revealed, reflects both the good and the bad of 2022 Starbucks Japan releases new summer drinkware range with Pegasus as the star
Starbucks Japan releases new summer drinkware range with Pegasus as the star 30 Okayama schools get postcards threatening to kidnap students
30 Okayama schools get postcards threatening to kidnap students Japan’s kanji character of the year for 2017 is “north”
Japan’s kanji character of the year for 2017 is “north” There’s a samurai-era village for you to walk through at this awesome overlooked museum in Japan
There’s a samurai-era village for you to walk through at this awesome overlooked museum in Japan
Leave a Reply