pollution
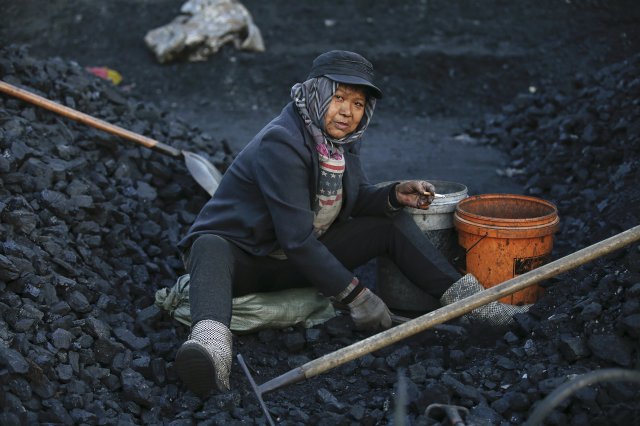
Global consumption of coal has declined significantly over the past year, driven by China, which makes up about half of the world’s demand for coal.
In a city in China’s southwestern Shichuan Province during the early hours of April 2, a man walking alongside the river suddenly noticed what appeared to be huge quantities of pale fish floating in the water.
He quickly rushed home and returned with fishing equipment, and was soon joined by crowds of amateur fishers – and local officials, who subsequently hauled 300 kilograms of fish from the river to be destroyed.
You may be familiar with oysters as the delicious seafood best eaten raw (or as ice cream) and served in months ending in “r,” but did you also know the little guys have impressive filtering skills that can clean even the dirtiest water?
Eating its fill of plankton and other particles floating around, a fully grown oyster can filter more than 50 gallons (189 liters) of seawater in one day. After seeing a few videos demonstrating this cleaning ability, some Japanese netizens started to question just how appetizing this made the once delicious-looking oyster.
Chinese cities have featured a lot in the news over the past few years. With the country experiencing rapid economic growth and its industries going into overdrive – though often with scant regard for the environment – the air quality in some cities has deteriorated to the point that health organisations have warned against spending too much time outdoors. The country’s rivers, too, bear the scars of progress as factories pump tons of waste into them, in some cases turning the water dark red.
Thankfully, though, the Chinese government has pledged to address the situation, and has this week announced plans to remove as many as six million vehicles from its roads in an effort to detoxify city air.
It’s well-known that China’s struggling with some serious air pollution, but perhaps less talked about is the toll being taken on their rivers. According to a recent survey conducted by Chinese media, 96% of respondents felt that not a single river around them was clean enough to swim in. And judging from these photos, anyone who did decide to risk a dive would probably come out looking worse than the Creature from the Black Lagoon.
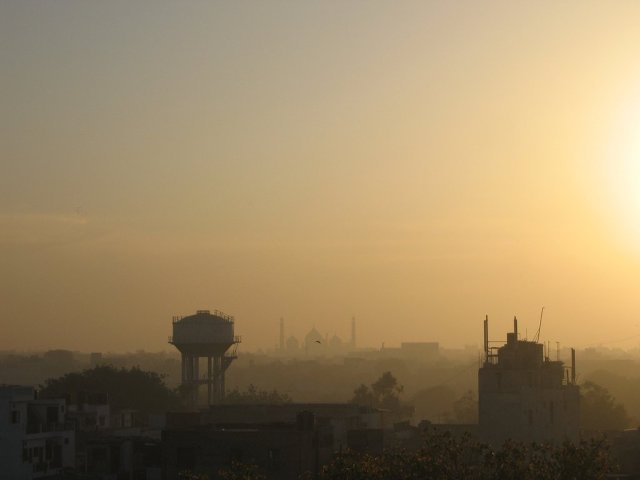
China’s smog — which routinely engulfs major cities like Beijing and Shanghai — is notorious, and it’s recently reached “danger levels.” But the the smog in New Delhi, The New York Times reports, is actually worse.
The air in New Delhi “is more laden with dangerous small particles of pollution, more often, than Beijing’s,” Gardiner Harris writes, and “a very bad air day in Beijing is about an average one in New Delhi.”
As if today being a Monday wasn’t depressing enough, media outlets are reporting that the air quality and visibility in China’s capital city has become so bad that the state has begun televising live footage of sunrises on enormous screens ordinarily used for advertising. That’s right: with the real thing now almost completely hidden behind a thick layer of smog, people are actually watching nature on TV.
As many of you may be aware, China has had some serious pollution problems in recent years with contamination spreading far and wide, affecting people’s health and everyday lifestyles. With all this negative publicity, it is of no surprise that China’s tourism industry has seen a decline in visitors to the country.
However, the Hong Kong Tourism Board has come up with a rather clever and, shall we say, peculiar scheme that guarantees to get rid of the smog, at least for all the tourists who want to capture a special photo for the occasion. It comes in the form of a picturesque banner of the Hong Kong landscape that is substituted for the real, polluted background. It’s just a case of standing in front of it, saying cheese and you’re done. Granted the picture may look good but it still doesn’t solve the actual problem of pollution.
Read More
According to the April 2 edition of Chinese daily newspaper the 21st Century Business Herald, in the year 2010 an incredible 1.23 million people lost their lives across China due to air pollution-related illnesses. The number accounts for 15 percent of total deaths recorded in the country for 2010. The information was revealed by a study group at Tsinghua University on March 31.
Read More
Recent reports from Radio France Internationale (RFI)’s Chinese site suggest that China’s pollution problem is raising serious concerns within the country itself. In the push for economic growth, the China is also becoming increasingly aware of what could potentially develop into a serious problem if steps are not taken soon. In this connection, there has been heated debate on the Internet suggesting that Chinese authorities are proposing moving the capital away from Beijing.
In recent years along with many other developing Asian nations, China has been increasing its level of industrial manufacturing as it readies itself for remarkable industrial growth. However, neglecting its environment for the sake of industry has brought with it the problem of dense smog pollution, with microscopic smog particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometres or less having been detected in overwhelming large amounts in China’s air in recent days.
The smog is the same as that found in factory exhausts, car fumes and the like. Measured per cubic meter, at one instance the observed value of pollution in Beijing reached levels 10 times the Chinese government’s recommended safety level. If one were to go by the Wealth Health Organization (WHO)’s recommended value, the figure rises to 40 times greater than normal. When it comes to pollution, it is thought that of the asian nations undergoing remarkable growth, 70% of nations are reaching a critical level. The toxic substances that seep out into the environment cause asthma, pneumonia and even in some cases death.
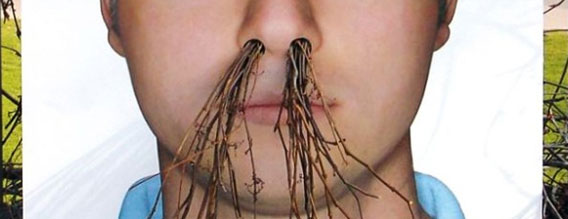
Of course, those living in highly polluted areas will surely want to know how their air compares, but measuring the levels each time can prove tiresome and expensive. With this in mind, one innovative company called Clean Air Asia has stumbled upon a way determine just how polluted your air is, and has designed an interactive map based on – wait for it – nostil hair.
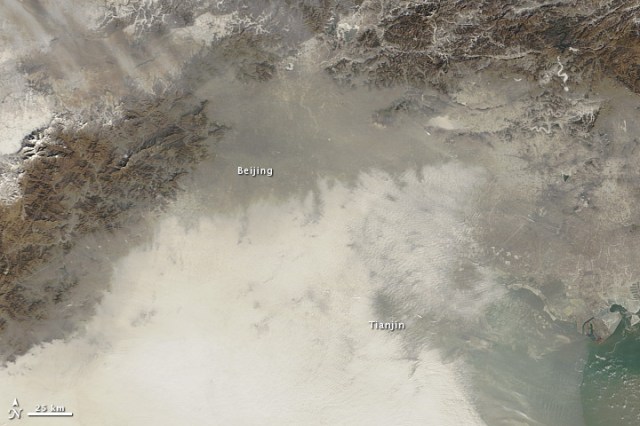
For days now Beijing has been suffering from a prolonged spell of the worst air pollution in the city’s history, a crisis so bad that it has been dubbed the “airpocalypse”.
The air has been classified as hazardous to human health and has already sent countless people to the hospital for respiratory ailments. The city is blanketed in a thick grey fog that is said to smell of coal and sting the eyes, leading officials to close highways, force the cancellation of flights and outdoor activities, and warn people in affected areas to remain indoors.
According to a researcher at Kyushu University, China’s giant toxic cloud of pollution is now expected to cross over to western Japan sometime later today.
The river you see here has been used by the residents of this part of Wenzhou, China daily for doing the wash. However, on the morning of 9 August they awoke to a puzzling sight.
The river had been dyed a milky white color overnight.







![Air quality in Beijing now so poor that sunrises are being broadcast on giant TV screens [UPDATED] Air quality in Beijing now so poor that sunrises are being broadcast on giant TV screens [UPDATED]](https://soranews24.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2014/01/screen-shot-2014-01-20-at-12-07-28-pm.png?w=640)



 Kyoto raises hotel accommodation tax to fight overtourism, travelers could pay up to 10 times more
Kyoto raises hotel accommodation tax to fight overtourism, travelers could pay up to 10 times more Viral Japanese cheesecake from Osaka has a lesser known rival called Aunt Wanda
Viral Japanese cheesecake from Osaka has a lesser known rival called Aunt Wanda Lawson adds doughnuts to its convenience store sweets range, but are they good enough to go viral?
Lawson adds doughnuts to its convenience store sweets range, but are they good enough to go viral? The best Hobonichi diaries, covers and stationery for 2026
The best Hobonichi diaries, covers and stationery for 2026 What makes this new Japanese convenience store chain better than 7-Eleven?
What makes this new Japanese convenience store chain better than 7-Eleven? The best cosplayers from Day Two of the Ikebukuro Halloween Cosplay Festival
The best cosplayers from Day Two of the Ikebukuro Halloween Cosplay Festival Haku is…Chihiro’s dead brother? Studio Ghibli fans blown away by Spirited Away theory
Haku is…Chihiro’s dead brother? Studio Ghibli fans blown away by Spirited Away theory Japan’s super easy sweet potato spread lets you make sweet potato bread thanks to Don Quijote
Japan’s super easy sweet potato spread lets you make sweet potato bread thanks to Don Quijote The Hayao Miyazaki anime we never got – New art book reveals Ghibli legend’s unrealized concepts
The Hayao Miyazaki anime we never got – New art book reveals Ghibli legend’s unrealized concepts What’s the deal with akebi, the perfectly purple, alien-like fruit that’s in season now in Japan?
What’s the deal with akebi, the perfectly purple, alien-like fruit that’s in season now in Japan? Starbucks Japan releases first-ever Hinamatsuri Girls’ Day Frappuccino
Starbucks Japan releases first-ever Hinamatsuri Girls’ Day Frappuccino Japanese restaurant chain serves Dragon Ball donuts and Senzu Beans this spring
Japanese restaurant chain serves Dragon Ball donuts and Senzu Beans this spring Highest Starbucks in Japan set to open this spring in the Tokyo sky
Highest Starbucks in Japan set to open this spring in the Tokyo sky Japan Extreme Budget Travel! A trip from Tokyo to Izumo for just 30,000 yen [Part 1]
Japan Extreme Budget Travel! A trip from Tokyo to Izumo for just 30,000 yen [Part 1] Japan has only one airport named after a samurai, so let’s check out Kochi Ryoma【Photos】
Japan has only one airport named after a samurai, so let’s check out Kochi Ryoma【Photos】 Japan Extreme Budget Travel! A trip from Tokyo to Izumo for just 30,000 yen [Part 2]
Japan Extreme Budget Travel! A trip from Tokyo to Izumo for just 30,000 yen [Part 2] Japan’s craziest burger chain takes menchi katsu to new extreme levels
Japan’s craziest burger chain takes menchi katsu to new extreme levels Japanese drugstore sells onigiri at pre-stupid era prices, but how do they compare to 7-Eleven?
Japanese drugstore sells onigiri at pre-stupid era prices, but how do they compare to 7-Eleven? Yakuzen ramen restaurant in Tokyo is very different to a yakuza ramen restaurant
Yakuzen ramen restaurant in Tokyo is very different to a yakuza ramen restaurant Tokyo Skytree turns pink for the cherry blossom season
Tokyo Skytree turns pink for the cherry blossom season Japan’s newest Shinkansen has no seats…or passengers [Video]
Japan’s newest Shinkansen has no seats…or passengers [Video] Starbucks Japan releases new sakura goods and drinkware for cherry blossom season 2026
Starbucks Japan releases new sakura goods and drinkware for cherry blossom season 2026 Foreigners accounting for over 80 percent of off-course skiers needing rescue in Japan’s Hokkaido
Foreigners accounting for over 80 percent of off-course skiers needing rescue in Japan’s Hokkaido Super-salty pizza sends six kids to the hospital in Japan, linguistics blamed
Super-salty pizza sends six kids to the hospital in Japan, linguistics blamed Starbucks Japan unveils new sakura Frappuccino for cherry blossom season 2026
Starbucks Japan unveils new sakura Frappuccino for cherry blossom season 2026 Foreign tourists in Japan will get free Shinkansen tickets to promote regional tourism
Foreign tourists in Japan will get free Shinkansen tickets to promote regional tourism The 10 most annoying things foreign tourists do on Japanese trains, according to locals
The 10 most annoying things foreign tourists do on Japanese trains, according to locals Take a trip to Japan’s Dododo Land, the most irritating place on Earth
Take a trip to Japan’s Dododo Land, the most irritating place on Earth Naruto and Converse team up for new line of shinobi sneakers[Photos]
Naruto and Converse team up for new line of shinobi sneakers[Photos] Is China’s don’t-go-to-Japan warning affecting the lines at a popular Tokyo gyukatsu restaurant?
Is China’s don’t-go-to-Japan warning affecting the lines at a popular Tokyo gyukatsu restaurant? Survey asks foreign tourists what bothered them in Japan, more than half gave same answer
Survey asks foreign tourists what bothered them in Japan, more than half gave same answer Japan’s human washing machines will go on sale to general public, demos to be held in Tokyo
Japan’s human washing machines will go on sale to general public, demos to be held in Tokyo Starbucks Japan releases new drinkware and goods for Valentine’s Day
Starbucks Japan releases new drinkware and goods for Valentine’s Day We deeply regret going into this tunnel on our walk in the mountains of Japan
We deeply regret going into this tunnel on our walk in the mountains of Japan Studio Ghibli releases Kodama forest spirits from Princess Mononoke to light up your home
Studio Ghibli releases Kodama forest spirits from Princess Mononoke to light up your home Major Japanese hotel chain says reservations via overseas booking sites may not be valid
Major Japanese hotel chain says reservations via overseas booking sites may not be valid Put sesame oil in your coffee? Japanese maker says it’s the best way to start your day【Taste test】
Put sesame oil in your coffee? Japanese maker says it’s the best way to start your day【Taste test】 No more using real katana for tourism activities, Japan’s National Police Agency says
No more using real katana for tourism activities, Japan’s National Police Agency says The best cosplayers from Day Two of the Ikebukuro Halloween Cosplay Festival
The best cosplayers from Day Two of the Ikebukuro Halloween Cosplay Festival Haku is…Chihiro’s dead brother? Studio Ghibli fans blown away by Spirited Away theory
Haku is…Chihiro’s dead brother? Studio Ghibli fans blown away by Spirited Away theory Japan’s super easy sweet potato spread lets you make sweet potato bread thanks to Don Quijote
Japan’s super easy sweet potato spread lets you make sweet potato bread thanks to Don Quijote The Hayao Miyazaki anime we never got – New art book reveals Ghibli legend’s unrealized concepts
The Hayao Miyazaki anime we never got – New art book reveals Ghibli legend’s unrealized concepts What’s the deal with akebi, the perfectly purple, alien-like fruit that’s in season now in Japan?
What’s the deal with akebi, the perfectly purple, alien-like fruit that’s in season now in Japan? Awesome Japanese sandals give you the footprints of a cat or T-rex
Awesome Japanese sandals give you the footprints of a cat or T-rex A Must-See Visual of Japan’s 2011 Earthquakes
A Must-See Visual of Japan’s 2011 Earthquakes Hey, 2020s kids! The ’90s have a sticker picture message waiting for you in Tokyo
Hey, 2020s kids! The ’90s have a sticker picture message waiting for you in Tokyo Tokaido ukiyoe series by Hiroshige now free to share, we celebrate with five favourites
Tokaido ukiyoe series by Hiroshige now free to share, we celebrate with five favourites Chance to play Teris on a massive staircase in Kyoto Station coming in March
Chance to play Teris on a massive staircase in Kyoto Station coming in March